Is Biometric Authentication always as safe as you thought
November 04, 2024
In response to escalating fraud and cyberattacks, biometric authentication has gained widespread acceptance globally. Yet, despite its seamless user experience, biometric systems are far from simple behind the scenes.

Authentication for computers dates back to the 1960s with the introduction of passwords. While simple by today's standards, passwords were a pivotal innovation, kickstarting a global movement toward safeguarding system access and data privacy.
Fast forward to today, authentication methods have evolved significantly, extending beyond basic account access to encompass multiple factors that better secure user identities. Since the rise of online banking in the early 2000s, financial institutions worldwide have adopted increasingly sophisticated customer authentication techniques to verify identities and prevent fraud. This demand has led to a proliferation of solutions, including password-based, two-factor, multi-factor, and biometric authentication, among others.
In response to escalating fraud and cyberattacks, biometric authentication has gained widespread acceptance globally. Yet, despite its seamless user experience, biometric systems are far from simple behind the scenes. Each solution varies in its technical complexity and the level of security it provides.
In this article, we will explore the different mechanisms used in biometric authentication, their strengths and weaknesses, and how businesses can choose the suitable solution for their platforms.
What is biometric authentication?
Biometric authentication refers to a process in cybersecurity that verifies a user's identity using their unique biological features like fingerprint, voice, retina, and face. During the process and throughout the account's lifetime, the biometric authentication systems store the user's information to verify their identity during account access. As a user, you can easily recognize biometric applications in smartphone unlocking, mobile APP login, and fund transfer transactions on banking APPs and websites.
Not only applied into mobile-friendly platforms, biometric authentication has been transforming airport security checks. Some of the world's busiest airports in Singapore, Dubai, and Spain are set to go all passport-free very soon. Experts have shared that the active implementation of biometric authentication technologies will help ease the immigration lines, while ensuring that foreign visitors are able to leave the country even in the case of lost passports.

Biometric Authentication isn't the same everywhere
In general, biometric authentication serves as an umbrella term for a method that can verify someone's identity through their biometric information (iris, fingerprint, voice, facial recognition). While a fingerprint and face recognition scan can look the same on various platforms, they aren't exactly the same. In recent years, many country governments have openly encouraged and mandated biometric as one of the verification options for state-provided and financial services like in Australia, Belgium, Canada, Denmark, Estonia, India, Netherlands, Nigeria, Singapore, Sweden, Thailand, Vietnam,and more. This approach has been growing in adoption and is well-received owing to its high level of convenience and security.

As authentication evolves, there are two main biometric authentication mechanisms that end-users likely interact with on a daily basis. They are server-side and client-side (on-device) authentication.
Server-side biometric authentication
This authentication mechanism takes place when the server provides certificates for authentication by the client. Majority of the process during server-side authentication is executed on the server, allowing for more complex data processing and analyzing capabilities.
Server-side biometric authentication is generally applied into login processes on digital platforms, electronic know-your-customer services where the user input must be referenced (matched) with a database on the server for verification. This type of biometric authentication mechanism is likely what you as a user would go through when opening a new banking account over the internet.
Client-side (on-device) biometric authentication
This authentication mechanism generally does not require passwords or secrets to be shared between the user and the public server. One of the most commonly known methods that implements on-device authentication is FIDO (Passkey), leveraging public key cryptographic tactics to ensure data security. In contrast with the former, because the authentication process itself happens entirely on-device, there are certain limitations to data processing and analyzing with client-side biometric authentication.
Most common use cases for client-side biometric authentication include digital platform login processes and online card payment authentication. With initiatives from global card brands such as Visa and Mastercard, FIDO with on-device biometric authentication is set to be the future of payments.
Which is the right choice for your platform?

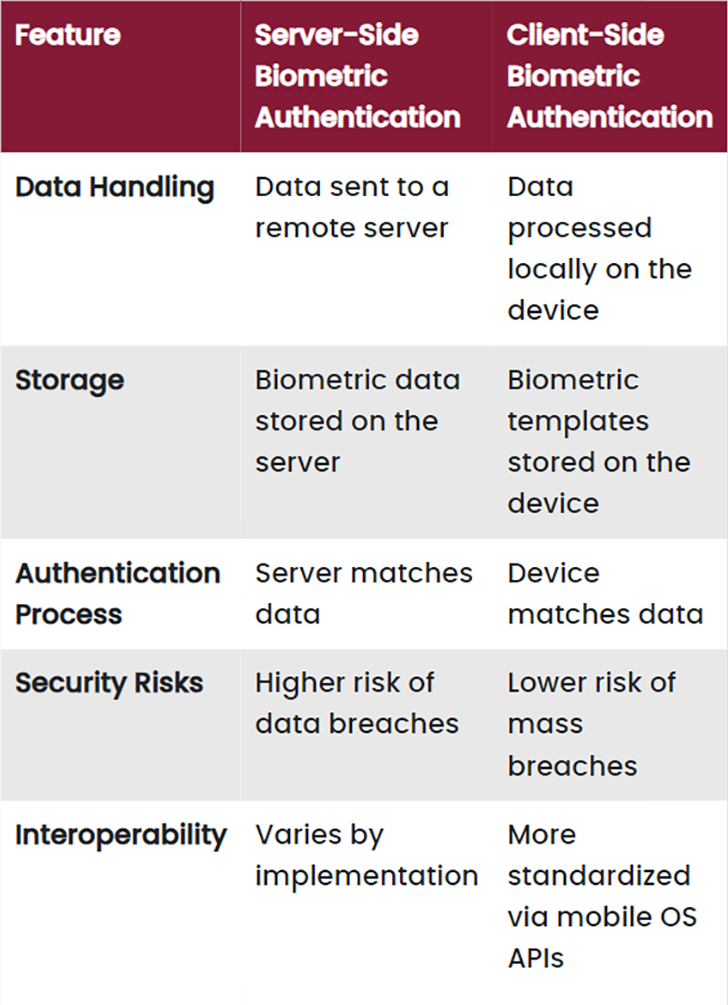
While offering different strengths serving specific purposes, the primary difference between server-side and client-side biometric authentication lies in where and how biometric data is processed and stored. Server-side authentication can offer advanced processing capabilities but comes with higher risks related to data security since the majority of the data is stored centrally. In contrast, client-side authentication emphasizes user privacy and security by keeping sensitive data local to the device, resulting in faster and often more secure authentication while being more limited on processing capabilities.
Below is a comparison table between the two mechanisms.
| Feature | Server-Side Biometric Authentication | Client-Side Biometric Authentication |
|---|---|---|
| Data Handling | Data sent to a remote server | Data processed locally on the device |
| Storage | Biometric data stored on the server | Biometric templates stored on the device |
| Authentication Process | Server matches data | Device matches data |
| Security Risks | Higher risk of data breaches | Lower risk of mass breaches |
| Interoperability | Varies by implementation | More standardized via mobile OS APIs |
As a solution provider, we always encourage our clients to thoroughly consider their purpose and needs for at least the below five features before deciding to choose either of the authentication mechanisms. For platforms that do not have concerns about data-sharing to a remote server and are interested to adopt more robust data processing and comparison algorithms. On the other hand, if your priority is to protect the platform, authentication activities against data breaches, enhance user privacy, and achieve faster response times, client-side biometric authentication is the way to go.
We offer FIDO through client-side authentication
From over 20 years of providing online payment authenticating solutions, we have been developing globally certified products and services, as well as ones that are entirely built by our in-house team. In recent years, the growing threats and losses from online fraud and scams have been alarming, prompting platform providers to reconsider their approach in navigating user authentication and system protection.
From our perspective, the interests and loyalty of end-users and customers are the biggest contributor to a business' success. Therefore, we believe in providing solutions that not only secure our clients, but also theirs, which prompted the introduction of our FIDO solution.
Leveraging on the power of public key cryptography mechanisms, in combination with globally certified open-source protocol specifications from the FIDO Alliance, we offer a secure and user-centric authentication solution, enabling platforms to go passwordless.
How does FIDO work?
Before being able to authenticate using FIDO, the user must go through the process of registration, in which a pair of public - private keys is generated specifically for a user account. While the private key is stored on the user device, the public key is safely kept on the public server; and both are end-to-end encrypted, ensuring security in the case of an attack.
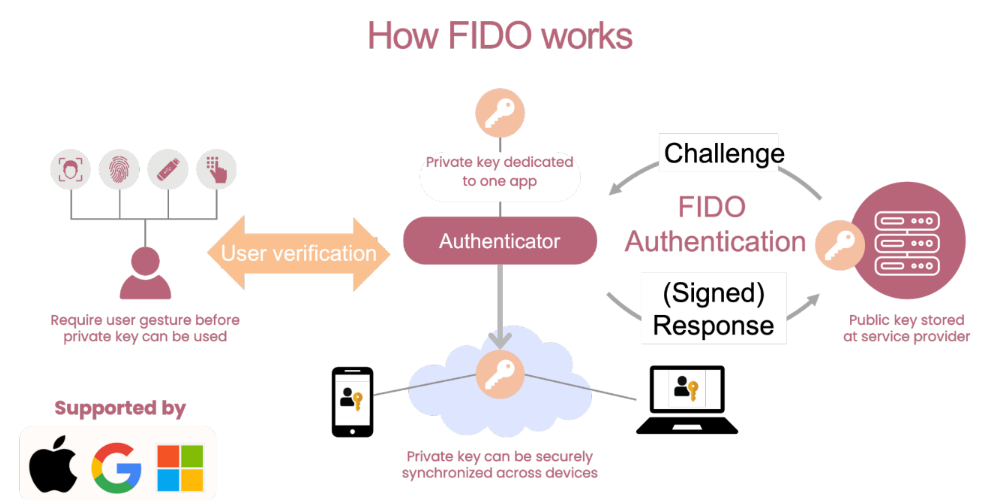
Taking advantage of a decentralized model, the biometric data is processed entirely on the user's device - such as a smartphone, security key, or computer that has a built-in biometric sensor. While being processed locally, the data is safeguarded by the device's secure hardware model (such as the Trusted Platform Module TPM) or Secure Enclave). Here, the private key is used to sign a cryptographic challenge from the server for identification. Correspondingly, the public key on the server is used to verify the response.
What are the security considerations?
Phishing-resistant: Since the private key and biometric data never leave the user's device, phishing attacks or server-side breaches cannot compromise the user's biometric information.
Local biometric processing: By keeping the biometric data processing local, the risk of data theft is minimized, even if the server is compromised.
No shared secrets: Unlike server-side biometric authentication, there are no shared secrets (e.g. biometric templates) between the client and server. This eliminates the risk of compromising sensitive biometric data stored on a centralized server.
Conclusion
To answer the question of “is biometric authentication the same everywhere?”, the simple answer is no. While there are countless solutions available in the market, they all serve authentication purposes along different pros and cons. When it comes to technology implementation on your platform, there is no right or wrong! However, effective and thorough consideration of the solution and technology will definitely make a difference on your system's security and customer experience.
As online threats continue to grow in both volume and complexity, timely adoption of preventive technologies is a must. At HiTRUST, we believe in supporting clients with the best of our expertise so you can concentrate on delivering exceptional products and services to your end-customers. Together, we will take on the challenges of online payment security and enter a new era of secure digital security.
To learn more, visit our official website, and schedule a call with us for an exclusive consultation for your platform's most meaningful authentication update.