What is OTP and why is it not as safe as you think?
December 20, 2023

Authentication happens every day when a user logs in to any platform, or a cardholder is trying to make a purchase online using his/ her credit card. OTP is the most common MFA method because it can be widely adopted - everyone has a phone, and ensures a certain degree of safety when it comes to identity verification.
However, as online fraud attacks evolve both tactic and volume wise, OTP is no longer your trusted friend. To frankly put, it's also far from being a convenient method of authentication.
In this article, we will be debunking what OTP actually is and the popular channels that it is delivered through, as well as why it is not as safe as you think, and suggest some alternatives that you could consider for your business.
What is OTP?
OTP, short for one-time password, is a string of characters referred to as a secret code automatically generated from a specific algorithm to authenticate a user for a single login or transaction.
With that said, OTPs are time-sensitive and will expire after use, whichever comes first. When compared to traditional static passwords, OTPs provide more security because the user will have to be a rightful owner of the receiving platform, in order to obtain the so-called secret code and proceed to verification.
Types of OTP
There are different types of OTP that businesses may choose to use for challenging their customers/users on specific platforms. The choice of OTP type often reflects common user behavior in the business' operating region as well as the preferred method of authentication by users.
Text Message OTP
Most widely used form of OTP. Sends the generated OTP to the user's mobile phone. It forms a critical part of the 2FA process, giving a secondary layer to the username and password.
Email OTP
This delivers the password to the user's registered email address. It's popular due to the high delivery rate and convenience. However, the safety of email OTPs rely on how well a user's email is protected from malicious attacks.
App-generated OTP
With growing adoption of smartphones, many businesses and services opt for an in-app OTP generation process, in which the user can link up with their various accounts and generate passwords accordingly. Another approach seen with this is where banks, for example, develop their own OTP generator app for their clients to generate and retrieve OTPs from, with every login or transaction made. The App can be further protected by a passcode to prevent illegitimate use of the generator.
Smartcard-based OTP
This type of generator is unique when compared to the rest. It works based on the "something you have" factor, which in this case is the card itself. This approach is often seen in banking and defense services to protect relevant activities. It works based on an embedded chip that can generate OTPs when come into contact with a card reader, which adds another layer of physical security to authentication.

How an OTP works
OTP authentication is an engagement between 2 sides, the user seeking authentication and the authentication server side looking to verify the user's identity. Both of them rely on a shared secret, which is the sequence passcode.
OTPs are oftentimes delivered to the user via a mobile device using an APP or SMS, or other channels such as an OTP token or a security key.
Why is it widely adopted?
Since it was first suggested by Leslie Lamport in the early 80s, OTP has been rapidly gaining popularity. It serves as a versatile method for authenticating users, while ensuring that widespread adoption is possible as more and more people possess a mobile phone to receive SMS OTP on.
Apart from SMS, email is also one easy way for users to receive their OTPs, especially when they can access their mailbox right from their smartphone. When compared with traditional passwords, an OTP is relatively safer because they cannot be reused or replayed.
Is OTP as safe as you think?
While no method is completely safe, OTP has been serving as an added layer to authentication. As technology develops and the internet space grows more complex, bad actors continuously discover different ways to pull off cyber attacks aimed at both the business and individual.
There are several ways in which OTP can be susceptible to attacks, which has been a concern for financial institutions, driving the active lookout for a safer and more convenient alternative.

Common OTP attacks
Bad actors can take advantage of OTPs in many ways, including code theft via SMS, SIM swap, and email hijacking. Below are the common ways in which hackers can use to capture a user's OTP for his/her own gains.
SMS Code Theft
Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks are no longer a new thing in the cyber world. Particularly with SMS messages attacking, Signaling System No. 7 (SS7) vulnerabilities have been giving attackers illegitimate access to telecommunication information, including the content of OTP delivery messages.
Besides SS7, scammers and fraudsters also attempt to steal user credentials through social engineering and phishing attacks. This is commonly seen in click-bait SMS, social media messages and emails where a counterfeit website is presented, tricking the genuine user to key in their personal information, and in turn, that data will be used on a real website for account takeover or fraudulent purchase.
SIM Swap
This kind of attack involves a malicious actor to conduct social engineering tricks to request a telecom company to transfer a customer's phone number to a different device and SIM card. In this case, the attacker has to collect specific customer's information that is convincing enough for the service company to fall into their trap.
Oftentimes, bribery comes into play to smoothen out and speed up the process. You might be surprised to know that 80% of SIM swap attacks are successful, as reported by a Princeton University's study.

Email Hacking
When implementing two-factor authentication, many companies opt for email instead of SMS due to the cost-effectiveness and the fact that they don't have to collect and store the user's mobile phone numbers during the registration process.
In most cases, email accounts are protected solely by a username and password. This means that attackers can hijack the account with MITM or social engineering attacks that would drive users to give up their OTP to bad actors and lose access to their accounts.
Any Alternatives?
If there's anything we hope you'd be able to take away from this article, it's that while OTP is still widely adopted, it is not as safe as you might think. Despite a growing awareness of the vulnerabilities, unfortunately, not many businesses are prepared for adopting other alternatives.
About five years ago, the National Institute of Standards of Technology in the US suggested that organizations begin deprecating OTP, especially via SMS. This signifies a strong urge not only to system and solution developers, but also businesses to start planning for the soon-to-happen change of authentication method, all for a safer online environment.
FIDO2 Authentication
FIDO (Fast Identity Online) is a set of open and standardized protocols for authentication, intended to facilitate the elimination of passwords. The protocols are developed and put forth by the FIDO Alliance, an industry association based in the US strongly supported by major members of the finance and technology realm such as Lenovo, Microsoft, Google, Apple, PayPal, EMVCo, W3C, Bank of America, and more.
According to reports presented by Alliance members at the Authenticate 2023 event held by FIDO Alliance in San Diego, FIDO2 authentication ensures a boastful 100% login success rate, achieving a 40% and 53% faster login speed compared to SMS OTP and email OTP respectively.
Authentication using the FIDO protocols function based on the concept of public key cryptography, involving a pair of public and private keys that are end-to-end encrypted. While the mechanism adopts public key infrastructure, with the public key stored on the public server and the private key stored solely on the user's device.
During authentication, challenges are sent and required to be signed by the private key, before being verified by the public key on the server. Owing to this infrastructure, user's credentials are safely guarded on their side, hence, presents no risk for MITM and phishing attacks.
Ever since its introduction, the FIDO standard has come a long way with over 100 certified products and to the enhanced version of 2.0, which supports more comprehensive authentication methods, while ensuring a safe, yet user-oriented process. Apart from that, the EMVCo and W3C has been working closely with FIDO Alliance to implement FIDO authentication into EMV 3-D Secure payments for the version 2.2 as well as the up-coming 2.3 version supported by Secure Payment Confirmation.
Up until November 2023, tech giants such as Google, Microsoft, Apple, Nintendo, Bank of America have successfully implemented FIDO authentication for their services across their websites and applications.
With FIDO authentication, users can experience secure and fast login across websites and applications without having to use a password. Instead, users can authenticate using the convenient, built-in biometric function on their mobile device, or using Windows Hello, PIN codes.
HiTRUST supports and provides FIDO authentication
While we are at the early stage of the migration from password to password-less, HiTRUST has always been in the forefront of innovation and development for security solutions made specifically for payments.
HiTRUST's FIDO solution presents a flexible application for both account login and payment authentication.
For Login
FIDO is applied into login authentication to verify the user without involving passwords. For each registered account, the relative device will store a private key that will sign off authentication challenges that are sent over from the public server. Before being able to authenticate, users must register their current account with FIDO right on the service provider's website or application. After that, each and every login can be done passwordlessly.
For Payment
From our consistent exposure and experience in providing authentication and security solutions for the banking and payment industry, we implement FIDO authentication into 3-D Secure transactions to help acquirers deliver a simpler, more seamless checkout experience.
Below is an example of HiTRUST's user interface for registration and authentication when making a purchase online.
The registration step happens after the customer places an order and completes their payment process. They will be prompted to a screen asking for preference of updating to FIDO.
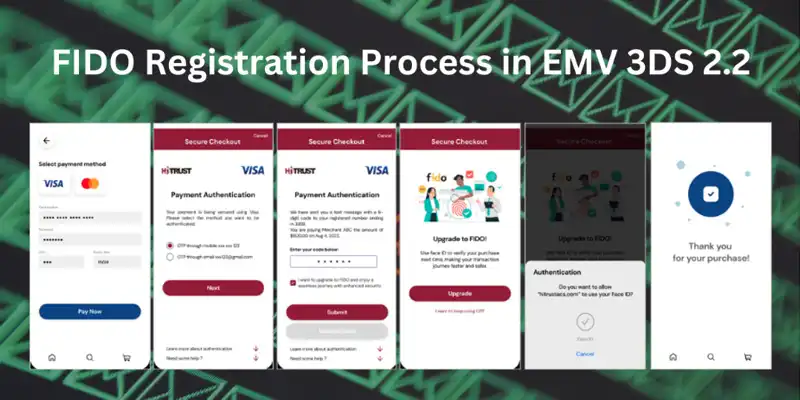
The next time the user makes a payment from the same online merchant, they will be able to choose FIDO as the authentication method, and in turn, the system will prompt the biometric scanning process to authenticate the payment.
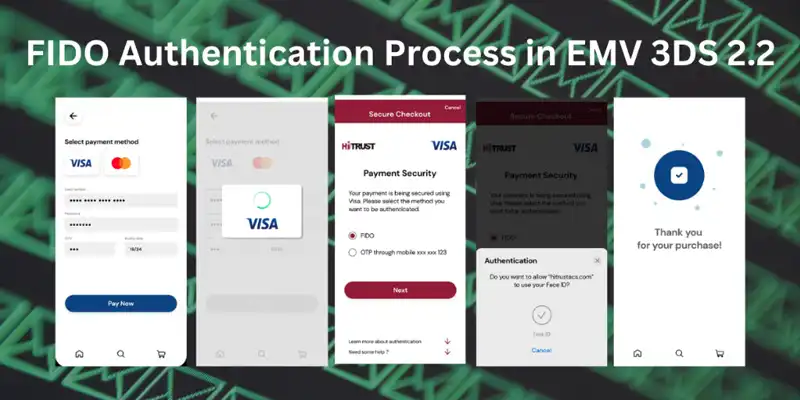
Conclusion
As we've learned, although OTPs are not the most attack-proof authentication method, they remain highly adaptable for businesses and account users around the world have grown accustomed to them over time.
In spite of that, there have been expert opinions indicating that to revolutionize account protection, passwords must be eliminated. Without the use of passwords to verify a user's account ownership, they will be much safer when faced with phishing or MITM attacks, as there will be no channel to conduct malicious activities on.
While it is only the beginning of the passwordless revolution, proactive preparation is crucial for your business to be one step ahead of any potential threat. Discover the benefits and use case scenarios of FIDO to begin your passwordless journey today.